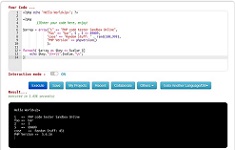
Python Operators
Python Tutorial » Python Operators
In Python Operators are special symbols that carry out arithmetic or logical computation
Example:
Output:
10
121
print(22 - 12)
print(47 + 74)
print(47 + 74)
Output:
10
121
Types of Operator
Arithmetic Operators
Comparison Operators
Assignment Operators
Identity Operators
Logical Operators
Membership Operators
Bitwise Operators
Arithmetic operators in Python
Example: Arithmetic operators are used with numeric values:
a + b = 16
a - b = 6
a * b = 55
a / b = 2.2
a // b = 2
a ** b = 161051
a = 11
b = 5
print('a + b =',a+b)
# Output: a + b = 16
print('a - b =',a-b)
# Output: a - b = 6
print('a * b =',a*b)
# Output: a * b = 55
print('a / b =',a/b)
# Output: a / b = 2.2
print('a // b =',a//b)
# Output: a // b = 2
print('a ** b =',a**b)
# Output: a ** b = 161051
Output: b = 5
print('a + b =',a+b)
# Output: a + b = 16
print('a - b =',a-b)
# Output: a - b = 6
print('a * b =',a*b)
# Output: a * b = 55
print('a / b =',a/b)
# Output: a / b = 2.2
print('a // b =',a//b)
# Output: a // b = 2
print('a ** b =',a**b)
# Output: a ** b = 161051
a + b = 16
a - b = 6
a * b = 55
a / b = 2.2
a // b = 2
a ** b = 161051
Comparison operators - examples
Comparison operators are used tot returns either True or False according to the condition.
Example: Comparison operators in Python
a > b is False
a < b is True
a == b is False
a != b is True
a >= b is False
a <= b is True
a = 12
b = 14
print('a > b is',a > b)
# Output: a > b is False
print('a < b is',a < b)
# Output: a < b is True
print('a == b is',a==b)
# Output: a == b is False
print('a != b is',a!=b)
# Output: a != b is True
print('a >= b is',a>=b)
# Output: a >= b is False
print('a <= b is',a<=b)
# Output: a >= b is False
Output: b = 14
print('a > b is',a > b)
# Output: a > b is False
print('a < b is',a < b)
# Output: a < b is True
print('a == b is',a==b)
# Output: a == b is False
print('a != b is',a!=b)
# Output: a != b is True
print('a >= b is',a>=b)
# Output: a >= b is False
print('a <= b is',a<=b)
# Output: a >= b is False
a > b is False
a < b is True
a == b is False
a != b is True
a >= b is False
a <= b is True
Identity Operators
In Python Identity operators are used to compare the objects, is and is not are the identity operators in Python
Example: Identity operators in Python
False
True
False
a1 = 12
b1 = 12
a2 = 'hi there'
b2 = 'hi there'
a3 = [1,2,3]
b3 = [1,2,3]
# Output: False
print(a1 is not b1)
# Output: True
print(a2 is b2)
# Output: False
print(a3 is b3)
Output:b1 = 12
a2 = 'hi there'
b2 = 'hi there'
a3 = [1,2,3]
b3 = [1,2,3]
# Output: False
print(a1 is not b1)
# Output: True
print(a2 is b2)
# Output: False
print(a3 is b3)
False
True
False
Python Operators math, precedence, overload, associativity, quiz, priority, and or, bitwise, order
Python Operators - python
Online Editor
This tool makes it easy to create, adjust, and experiment with custom colors for the web.
HTML Templates
Magnews2 is a modern and creative free magazine and news website template that will help you kick off your online project in style.
CSS HTML Layout
Find here examples of creative and unique website layouts.
Free CSS HTML Menu
Find here examples of creative and unique website CSS HTML menu.